So you’re interested in homebrewing beer? Well, if you want to master the art of brewing, one crucial element that you need to understand is pH and its importance. pH plays a vital role in determining the quality, flavor, and overall success of your brew. It affects everything from the enzymatic reactions during mashing to the fermentation process. By grasping the significance of pH in brewing, you’ll be able to create brews that are not only delicious but also consistent and well-balanced. In this article, we will delve into the world of pH and explore its implications in the fascinating realm of homebrewing.
What is pH?
pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a substance is on a scale of 0 to 14. It indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 are acidic and those above 7 are alkaline. In the context of brewing, pH plays a crucial role in determining the quality, flavor, and characteristics of beer.
pH Scale
Definition
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Each whole number difference on the scale corresponds to a tenfold difference in acidity or alkalinity. For example, a solution with a pH of 5 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 6.
Measurement
pH is measured using a pH meter or pH test strips. A pH meter consists of a probe that is submerged in the liquid being measured. The probe sends an electrical signal to the meter, which then calculates and displays the pH value. pH test strips are paper strips treated with chemicals that change color depending on the acidity or alkalinity of the solution. The color change is then matched with a color chart to determine the pH value.
Why pH is Important in Brewing
pH plays a critical role in every step of the brewing process. It affects enzyme activity during mashing, yeast health and activity during fermentation, as well as flavor development and overall quality control. Maintaining the optimal pH throughout brewing ensures the desired characteristics and taste of the final product.
Mashing Process
Enzyme Activity
During mashing, the enzymes in the malted grains convert starches into fermentable sugars. The enzymatic activity is greatly influenced by pH, with different enzymes having different optimal pH ranges. If the pH is too high or too low, the enzymes may not function optimally, leading to incomplete conversion of starches and ultimately affecting the flavor and body of the beer.
Extract Efficiency
pH also affects the extract efficiency of the grains. A pH within the ideal range helps maximize the extraction of sugars, flavor compounds, and other desirable elements from the grains. This ensures that the brewer achieves the desired gravity and flavor profile of the wort.
Lautering
Lautering, the separation of the liquid wort from the grain bed, is impacted by pH as well. Improper pH levels can cause the grain bed to compact or become sticky, leading to reduced wort flow and lower efficiency during the lautering process. Maintaining the correct pH can help prevent these issues and facilitate a smoother lautering process.
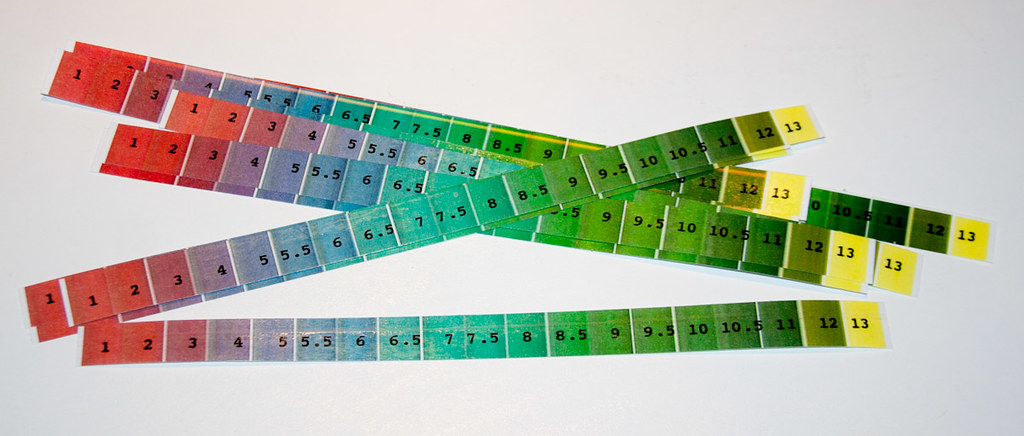

Fermentation Process
Yeast Health and Activity
pH plays a vital role in yeast health and activity during fermentation. Yeast growth and metabolism are greatly influenced by the pH of the wort. Maintaining the correct pH level helps create an environment that promotes healthy yeast growth and efficient fermentation. An improper pH can stress the yeast, leading to sluggish or stuck fermentation, off-flavors, and even the growth of harmful bacteria.
Flavor Development
The pH of the wort and subsequent beer can also impact flavor development. Different flavors are extracted from the hop compounds and other ingredients at different pH levels. The acidity of the wort affects the balance between sweet and bitter flavors, and even subtle variations in pH can result in noticeable changes to the final flavor profile of the beer. Maintaining the optimal pH helps ensure the desired flavor balance and character.
Quality Control
Monitoring pH throughout fermentation is essential for quality control. It allows brewers to detect and correct any pH imbalances that could lead to off-flavors or inconsistencies in the beer. Additionally, pH monitoring can help identify any potential contamination issues early on, enabling prompt corrective action to maintain the quality and integrity of the final product.
Acidification and pH Adjustment
Water Treatment
Water plays a crucial role in brewing, and its pH can significantly impact the final pH of the beer. Treating water to achieve the desired pH is often necessary to ensure optimal conditions for brewing. This can involve the addition of acids or alkaline substances to adjust the pH and bring it within the desired range.
Sour Beers
For brewers looking to create sour beers, pH becomes even more critical. Sour beers are known for their tart and acidic flavors, and achieving the appropriate level of acidity requires careful control of pH throughout the brewing process. Manipulating the pH during mashing, fermentation, or aging can enhance the production of lactic acid and other souring agents, resulting in the desired sour beer characteristics.

Testing and Monitoring pH
Equipment
To accurately measure and monitor pH, various equipment options are available to brewers. pH meters are commonly used and provide precise readings, making them ideal for professional brewers or serious homebrewers. pH test strips, on the other hand, offer a more affordable and accessible option for casual homebrewers, although they may not be as accurate as pH meters.
Sampling Techniques
When testing pH, it is important to ensure representative samples are obtained. This involves taking samples from different parts of the brewing process, such as the mash, wort, or fermenting beer. Sampling at various stages allows brewers to understand how pH changes throughout brewing and can help identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Correcting pH Imbalances
If pH measurements indicate that the pH is out of the optimal range, corrective actions may be required. This can involve adjusting the pH using food-grade acids or alkaline substances. Brewers must be cautious when making adjustments, as even small changes can have significant impacts on the final product. Gradual adjustments are often recommended to avoid overshooting the desired pH.
Optimal pH Ranges for Brewing
Mashing pH
The optimal pH range during mashing is typically between 5.2 and 5.6. This range provides the ideal conditions for enzymatic activity, maximizing starch conversion and preventing undesirable flavors. Brewers can use pH meters or test strips to monitor the pH during mashing and make adjustments as necessary.
Wort pH
During the boil and cooling of the wort, the pH may change slightly. However, it is generally recommended to maintain a pH range of 5.2 to 5.6. This range continues to support enzymatic activity and helps create an environment conducive to yeast health during fermentation.
Fermentation pH
The ideal pH range for fermentation varies depending on the style of beer being brewed. In general, a pH range of 4.0 to 4.5 is desired, as it promotes a healthy fermentation process and contributes to the desired flavor profile. Some beer styles, such as sour beers, may have lower pH requirements to achieve their characteristic acidity.
pH Troubleshooting
Off-Flavors and Off-Aromas
Off-flavors and off-aromas in beer can often be attributed to pH imbalances. Sour or vinegary flavors may indicate a low pH, while a harsh bitterness can be a result of high pH levels. Monitoring and adjusting pH can help mitigate these undesirable flavors and achieve a more balanced and enjoyable beer.
Inconsistent Results
If brewing results vary from batch to batch, pH imbalances could be a contributing factor. Inconsistent pH can lead to variations in enzymatic activity, hop utilization, fermentation performance, and flavor development. Monitoring and maintaining the optimal pH from one batch to the next can help ensure more consistent and predictable results.
Conclusion
Understanding and monitoring pH throughout the brewing process is essential for producing high-quality, flavorful beer. pH influences enzyme activity during mashing, yeast health and activity during fermentation, and the overall flavor profile of the beer. With proper pH control and adjustment, brewers can create beers that meet their desired specifications and consistently deliver a satisfying drinking experience. So next time you embark on a brewing adventure, remember the significance of pH and its role in crafting the perfect pint. Cheers to brewing success!
© 2024 by Brew Info Reserved all rights. This document cannot be copied or communicated in any way without Diettips.net’s prior written consent, whether it be electronically, mechanically, through photocopying, recording, or another medium.